What Is Non-Destructive Testing?
As its name implies, non-destructive testing, or NDT, consists of a series of tests to determine the conformance of metal castings to a specific set of standards. NDT identifies faulty or compromised parts before they go through further processing, often leading to upgrade repairs or even full rejection. The use of NDT at this stage of the processing identifies areas of concern before failure of the critical application component can occur.
Destructive Testing Versus Non-Destructive Testing
The main difference between non-destructive testing and destructive testing is that the cast component itself is not lost or compromised as a result of the test. All NDT tests are “non-invasive” by design, whereas a destructive test would result in the casting being “sectioned” to remove the test pieces for evaluations, rendering the actual casting unable to be used in its intended application.
Destructive testing would include such activities as selecting a random casting from a batch or “heat” of metal poured, and having the base metal machined into a tensile test specimen to be pulled apart to measure the mechanical strength of the alloy, a Charpy impact specimen to be machined and then broken to measure toughness, or to perform corrosion testing on specimens obtained from various parts of the casting. In some cases, destructive testing will involve sectioning a casting and looking for signs of shrinkage defects when the cost of NDT is restrictive.
Advantages of Non-Destructive Testing
The obvious advantage of non-destructive testing is that the casting is not lost to the testing process. This results in cost savings to the customer. Further, when appropriate for the purpose, the test is specific to that component, rendering the ability for Niagara Investment Castings to certify that that exact casting meets the clients’ specifications individually, rather than the results of the NDT tests being considered representative to a “batch” of castings.
Types of Non-Destructive Tests
While there are many types of NDT tests, those most prevalent in the foundry industry are Radiography, Liquid Penetrant Testing, and Magnetic Particle Testing. These are most conducive to the general characteristics of the investment casting process.
Other NDT tests not as commonly used for castings include Ultrasonic Testing and Eddy Current Testing.
Radiography
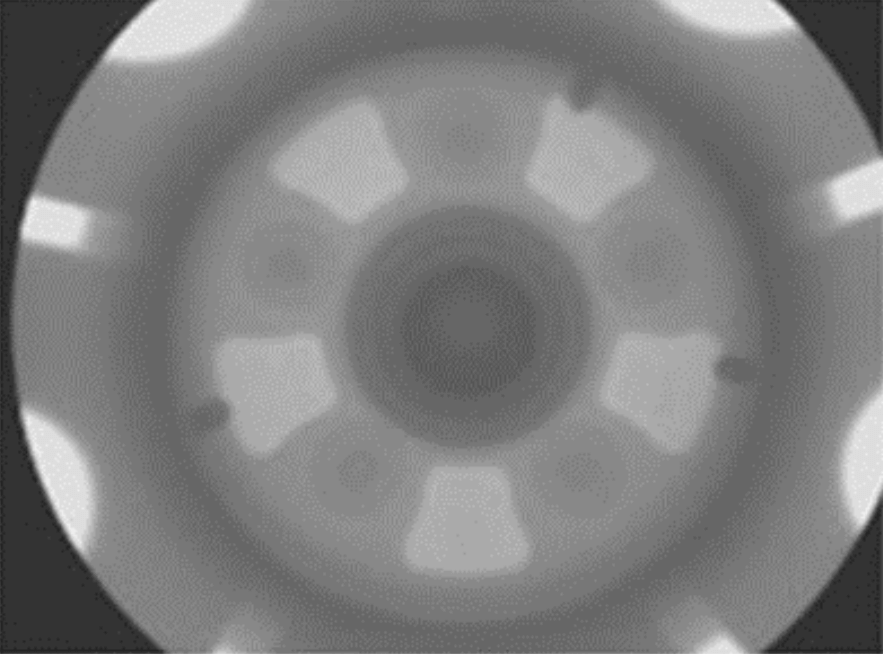
Radiographic Testing (RT) is a very commonly applied non-destructive testing method used to inspect the internal structure of metal castings for shrinkage or other porosity-type defects, as well as inclusions and cracks.
This testing method uses X-rays to penetrate the metal and create an image of the internal structure on film or digital media. The resulting radiographic image allows inspectors to detect a range of flaws, including cracks, voids, inclusions, and other irregularities that may affect the quality and safety of the metal component.
Radiographic testing of investment castings is generally considered as an evaluation of material properties. Material property evaluation includes determining composition, density, uniformity, and cell or particle size, as well as flaws (voids, inclusions, and cracks) in the casting that are not obvious at the surface, or after machining to remove material from the casting.
Radiographic testing is widely used in demanding industrial sectors to ensure the safety and reliability of critical cast components.
Liquid Penetrant Inspection
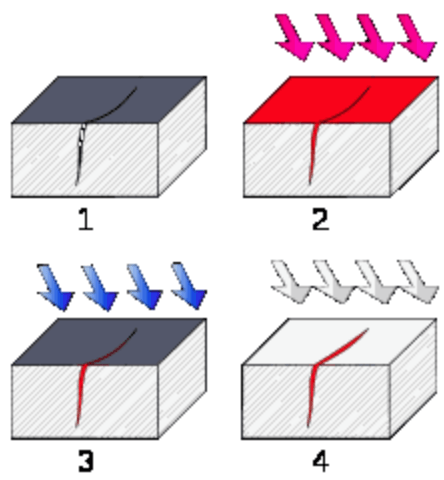
During the metal casting process, tiny cracks, pores, and other surface imperfections can occur that cannot be seen during a visual inspection. Liquid penetrant testing is used to find these flaws in castings made from most any of the alloys we can offer.
After cleaning the metal casting, a liquid penetrant is applied and drawn into any flaws by capillary action. The penetrant can either be a red dye, or a fluorescent type viable under black light. The part is then washed, dried, and a developer applied to the same surfaces to “draw” the penetrant back out to reveal where there are any surface flaws.
Once the testing is complete, the results are recorded and indications marked or catalogued, and the casting is thoroughly cleaned of any residue left behind.
Magnetic Particle Testing
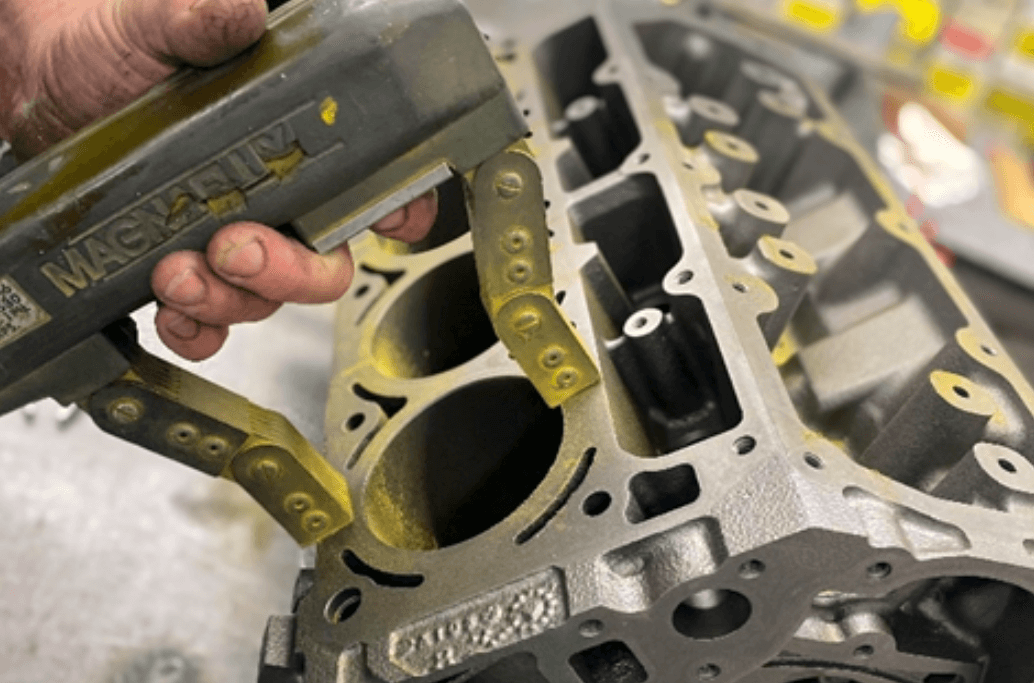
Applicable to ferromagnetic metal casting containing iron or steel, magnetic particle inspection detects surface or near-surface discontinuities on the component, such as cracks or fine fissures.
This process involves inducing a magnetic field via an electric current around the component. When a discontinuity is present, the magnetic field is disrupted. We interpret and evaluate these indications, record the results and/or mark the castings, and then clean the metal casting of any residue left behind by the examination.
Applications for Non-Destructive Testing

There are many times when non-destructive testing is required by the customer, to ensure either batch conformance, or individual casting certifications, to their specific standard. Examples of industries which rely on our providing certified NDT results of our castings include:
- Nuclear Power Industry
- High-Pressure Pumps and Valves
- Military applications such as Submarines, Ships, and Armoured Vehicles
- Aerospace
- Oil and Gas Equipment
- Chemical Processing Equipment
Choose Niagara Investment Castings for Your Critical Casting Applications
Niagara Investment Castings produces castings for many applications, from simple hardware and machinery parts to critical cast components used in nuclear applications, defence systems, and high-pressure pumps, valves, and vessels. Many of these critical application castings require verification of the internal integrity of the casting without compromising the casting itself. In these situations, non-destructive testing provides the means to obtain that crucial information for our clients.
